How Does Fiber Optic Work?
Date: 2024-08-25
The light and its properties
Light is an electromagnetic wave. The visible part of the wavelength range is from 390 a 760 nm. The part of the light above 760 nm is infrared and the lower than 390 nm is ultraviolet. The three most commonly used wavelengths in optical fibers are 850, 1310 Y 1550.
Refraction and Reflection of Light
Light travels at different speeds in different substances.. When light is directed from one substance to another, is refracted and reflected at the interface between the two substances. The angle of the refracted light varies with the angle of the incident light.. When the angle of incident light reaches or exceeds a certain angle, all incident light is reflected, what is called total reflection of light.
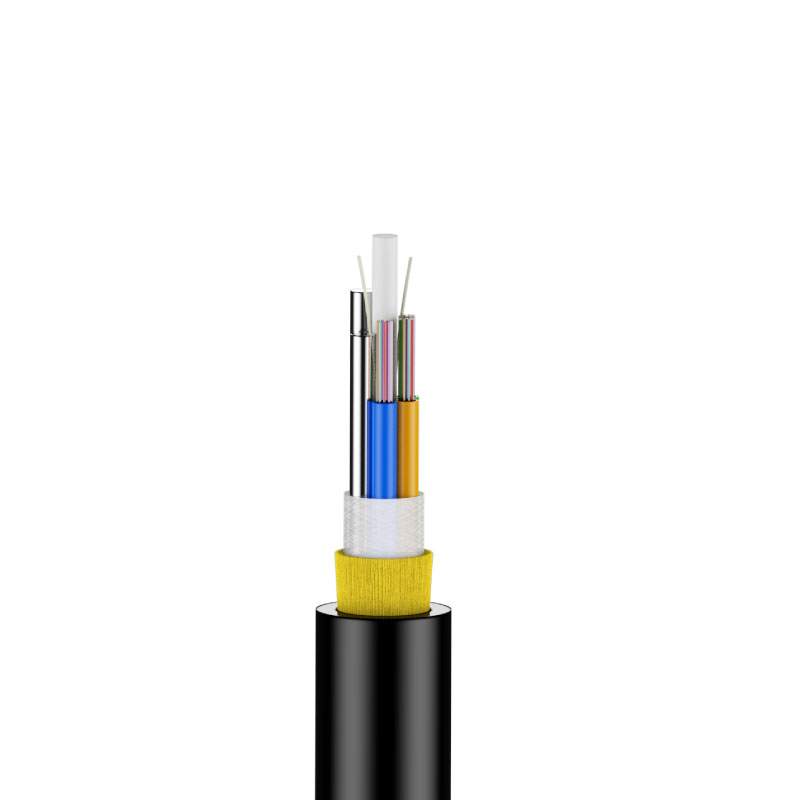
Fiber optic communication is based on these principles. The main part of an optical fiber is usually divided into three layers. In the center is a high refractive index glass core. And on the outer layer there is a low refractive index silica glass coating. The outermost layer is a reinforcing resin coating.
Optical Signal Conversion
The optical transmission system consists of three components: the light source, the transmission medium and the detector. It is common for a pulse of light to represent the bit 1 and that no pulse of light represents the bit 0. When light hits the detector, produces an electrical pulse. With a light source at one end of the fiber and a detector at the other, a one-way transmission system is formed. Receive an electrical signal, converts it into a light impulse and transmits it, and then the receiving end converts the light impulse back into an electrical signal.